Ethinyl Estradiol, Low Dose Oral Contraceptives
Dr. Álvaro Monterrosa Castro, MD
lEfforts to improve the quality of oral contraceptives have been aimed at further reducing the concentration of Ethinyl Estradiol. (5.25). This seeks to reduce risks and minimize adverse reactions. Both biochemical and clinical characteristics of these preparations. And at the same time preserve contraceptive efficacy and non-contraceptive benefits (25, 213).
Furthermore, it is important to remember that minor or serious adverse reactions are directly related to discontinuation of the method.
First, clinical and epidemiological studies (214, 215)and especially the one advanced by Endrikat J, et al (213). They confirm that it is possible to minimize the risks and improve the acceptability of oral contraceptives. Without negatively affecting contraceptive effectiveness. Decreasing the concentration of Ethinyl Estradiol to 20 Ug per tablet.
(Read Also: Concepts in Oral Contraceptives – Beneficial Effects)
Leading to replacing the old concept that 30 Ug of Ethinyl Estradiol constituted the minimum necessary daily dose. That combined with a Gestagen had acceptable effectiveness from a contraceptive point of view.
Second, since 1973, Loestrim 1/20 has been available in some countries, which combines 20 Ug of Ethinyl Estradiol with 1 mg of Norethisterone Acetate. (25). In the 1980s, studies were carried out with preparations that included 20 Ug of Ethinyl Estradiol plus Gonans, in the first instance Desogestrel. At IFFS-95 in Mompellier, France. Works were presented using Gestodeno (214,215).
Heuner A.
Likewise, Heuner A. et al (216) have performed pharmacokinetic studies with this very low dose combination. Winkler UH et al (5) At the same time, they studied the effects on the hemostatic system of the combination of 75 Gestodene and 20 Ethinyl Estradiol. And they conclude that it has a balanced effect on hemostasis. Stimulating both the pro-coagulation system, anticoagulant and fibrinolytic activity. When their results were compared with the combination of 75 Gestodene and 30 Ethinyl Estradiol. They obtained similar considerations, with non-significant statistical differences (5).
Consequently, metabolic parameters do not seem to be significantly affected by oral contraceptives containing 20 or 30 Ug of Ethinyl Estradiol. (217).
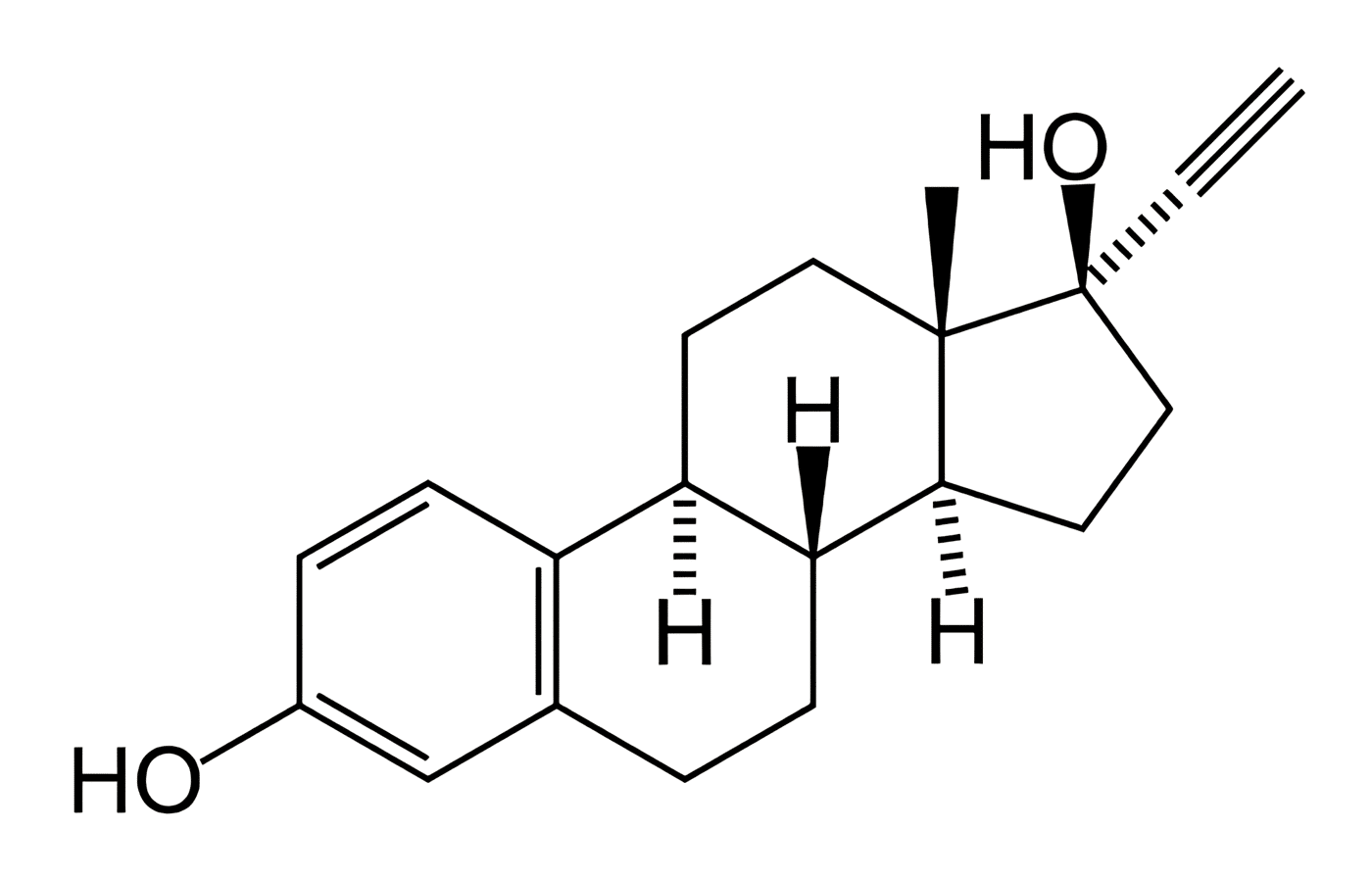
Gestodene, which has greater antigonadotrophic activity than Norethindrone, Norgestimate, Desogestrel or Levonorgestrel. Which has a very low androgenicity and therefore little deleterious effect on lipids, and very minimal estrogenic activity. When used in combination with 20 Ug of Ethinyl Estradiol, it provides a hormonal balance very close to the ideal, which makes it an interesting alternative for the late 20th century.
Likewise, by early 1988 the most extensive multicenter phase III investigation to date (214).
An open, non-comparative study carried out on 19,095 cycles of use in 670 women for 36 cycles each. It established a Pearl index of 0.07. Which confirms the great contraceptive effectiveness of the combination Ethinyl Estradiol 20 Ug plus Gestodene 75 Ug. There are already comparative studies between this pill and another that combines Ethinyl Estradiol 20 Ug plus Desogestrel 150 Ugs. Where the good effectiveness of both repairs is confirmed (215).
It should be noted that a certain percentage of women who receive very low-dose combined oral contraceptives present intermenstrual bleeding or spotting. Especially in the first six cycles of pill use. We must inform the patient of this fact, which is related to the low dose administered. To avoid unnecessary worries in patients, which leads to abandonment of the use of the method (213,215).
Transhormonal bleeding is usually much more frequent in the first cycles of use. Dusterberg (214) points out that there is a gradual decrease in the incidence of these bleeding episodes.
Furthermore, Short (215) has compared the 20 Ug tablets of Ethinyl Estradiol that include Desogestrel with those that include Gestodene. Noting that both spotting and intermenstrual bleeding occur more frequently with the former. But in both combinations the frequency of these episodes gradually decreases.
Irregular intake of the very low-dose preparation considerably increases the rates of transhormonal bleeding. Therefore we must insist on correct intake. In addition, incorrect intake is also related to an increase in method failure rates. Adverse symptoms are markedly reduced by reducing estrogen concentration.
Dusterberg B.
Finally, Dusterberg B. et al (214) compared the adverse symptoms when administering 20 Ug Ethinyl Estradiol + 75 Ug Gestodene pills with 30 Ug Ethinyl Estradiol and 75 Ug Gestodene pills. Finding respectively: headaches: 15.7% and 25.9%. Breast tension: 8.4% and 19.7%. Nervousness: 4.2% and 17%. Nausea: 3.7% and 13.5%. Vertigo: 3.3% and 10.1%, Depression: 1.2% and 7.9%. Varicocities: 0.7% and 4.4.%.
Therefore, these findings support that reducing the intake of Ethinyl Estradiol may be associated with a lower incidence of adverse effects, which some call minor. But they usually affect the quality of life or interfere with the woman’s routine activities. Which leads to abandonment of the use of the method.
Finally, Michael Gast at the XV FIGO World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Copenhagen in August 1997. He argued that the 20 Ug Ethinyl Estradiol pill is effective in inhibiting ovulation without evidence of escape ovulation.
In conclusion, this author considers that the new very low dose pills provide excellent contraceptive safety, with a minimal impact on metabolic parameters.